Generative Modeling of Multi-mapping Reads with mHi-C Advances Analysis of High Throughput Genome-wide Conformation Capture Studies
Abstract
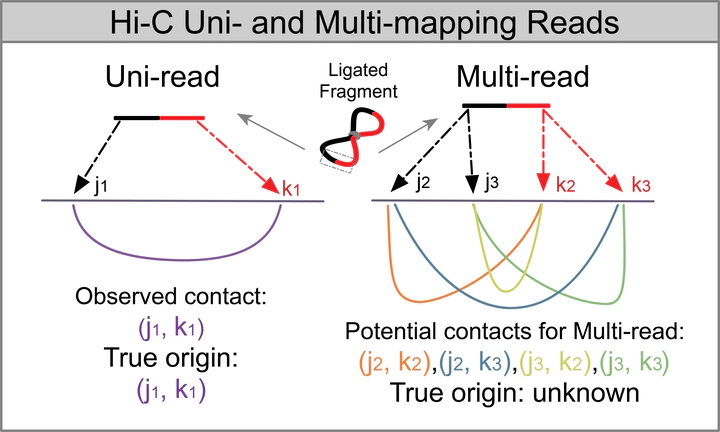
Current Hi-C analysis approaches are unable to account for reads that align to multiple locations, and hence underestimate biological signal from repetitive regions of genomes. We developed and validated mHi-C, a multi-read mapping strategy to probabilistically allocate Hi-C multi-reads. mHi-C exhibited superior performance over utilizing only uni-reads and heuristic approaches aimed at rescuing multi-reads on benchmarks. Specifically, mHi-C increased the sequencing depth by an average of 20% resulting in higher reproducibility of contact matrices and detected interactions across biological replicates. The impact of the multi-reads on the detection of significant interactions is influenced marginally by the relative contribution of multi-reads to the sequencing depth compared to uni-reads, cis-to-trans ratio of contacts, and the broad data quality as reflected by the proportion of mappable reads of datasets. Computational experiments highlighted that in Hi-C studies with short read lengths, mHi-C rescued multi-reads can emulate the effect of longer reads. mHi-C also revealed biologically supported bona fide promoter-enhancer interactions and topologically associating domains involving repetitive genomic regions, thereby unlocking a previously masked portion of the genome for conformation capture studies.